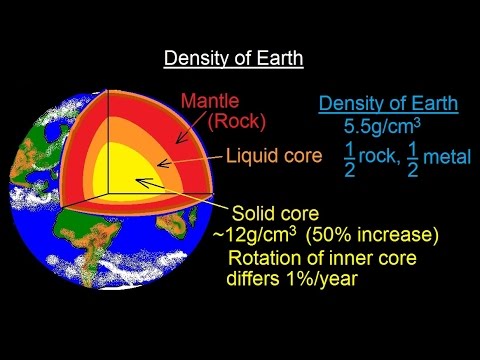
Earth’s average density is 5.52 grams per cubic centimeter. This makes it the densest planet in our solar system.
Earth’s density plays a crucial role in its gravitational pull. The planet’s dense core consists mainly of iron and nickel. This core is surrounded by a mantle rich in silicate minerals. These layers contribute to Earth’s overall density. Understanding Earth’s density helps scientists study its internal structure.
It also aids in learning more about plate tectonics and volcanic activity. Earth’s density affects its magnetic field, essential for protecting life from harmful solar radiation. Researchers continually study Earth’s density to gain insights into its formation and evolution. This knowledge is vital for both geology and planetary science.

Credit: www.ck12.org
Earth’s Composition
The Earth is a complex and diverse planet. Its composition influences its density, structure, and behavior. Understanding the Earth’s composition helps us learn more about our planet’s formation and evolution. This section delves into the various layers and elements that make up the Earth.
Layers Of The Earth
The Earth is divided into several layers. Each layer has distinct properties and compositions. The main layers include:
- Crust: The outermost layer, which is solid and thin.
- Mantle: Located beneath the crust, it is semi-solid and much thicker.
- Outer Core: A liquid layer made of molten metals.
- Inner Core: The innermost layer, solid and composed mainly of iron.
Materials And Elements
Different materials and elements make up each layer of the Earth. The crust contains rocks, minerals, and organic materials. Common elements in the crust include oxygen, silicon, and aluminum.
The mantle consists mostly of silicate minerals, rich in iron and magnesium. The outer core is primarily composed of liquid iron and nickel. The inner core is solid due to extreme pressure and mainly made of iron.
Here is a table summarizing the primary materials and elements in each layer:
| Layer | Primary Materials | Key Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Crust | Rocks, Minerals | Oxygen, Silicon, Aluminum |
| Mantle | Silicate Minerals | Iron, Magnesium |
| Outer Core | Molten Metals | Iron, Nickel |
| Inner Core | Solid Metal | Iron |
Understanding these materials and elements provides insights into the Earth’s density. Each layer’s composition affects its density and overall structure. This knowledge is crucial for geologists and scientists studying our planet.
Measuring Density
Understanding the density of Earth helps scientists learn about its composition. Density is mass per unit volume. Earth’s density tells us about its inner structure. Let’s explore how scientists measure Earth’s density.
Methods And Tools
Scientists use various methods and tools to measure Earth’s density. One common method is the gravitational method. It involves measuring the gravitational force between two objects. These measurements help calculate Earth’s density.
Another tool used is the seismograph. Seismographs record seismic waves from earthquakes. These waves travel through Earth’s layers at different speeds. By analyzing these speeds, scientists infer the density of each layer.
There is also the hydrostatic method. This method measures the pressure at different depths in Earth’s oceans. The pressure data helps determine the density of the Earth’s crust and mantle.
Historical Approaches
In the past, scientists used simpler methods to estimate Earth’s density. One famous method was the Cavendish experiment. In 1798, Henry Cavendish used a torsion balance to measure the gravitational pull between lead spheres. This experiment provided an early estimate of Earth’s density.
Another historical approach involved pendulum experiments. Scientists measured the period of a pendulum at different locations. Variations in the period indicated differences in gravitational force. These differences helped estimate Earth’s density.
Early astronomers also used the orbital motion of the Moon and planets. By observing their motions, they could estimate the mass of Earth. Knowing the volume of Earth, they then calculated its density.
| Method | Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Gravitational Method | Gravitational Force Measurement | Calculate Earth’s Density |
| Seismograph | Seismic Wave Analysis | Infer Layer Density |
| Hydrostatic Method | Pressure Measurement | Determine Crust and Mantle Density |
| Cavendish Experiment | Torsion Balance | Early Density Estimate |
| Pendulum Experiments | Pendulum | Estimate Gravitational Force |
Core Characteristics
The Earth’s core holds many secrets about our planet. It influences Earth’s magnetic field and heat flow. Understanding the core’s characteristics reveals why Earth is so dense.
Inner Vs Outer Core
The Earth’s core has two parts: the inner core and the outer core.
| Feature | Inner Core | Outer Core |
|---|---|---|
| State | Solid | Liquid |
| Composition | Iron and Nickel | Iron and Nickel |
| Depth | 5,150 – 6,371 km | 2,890 – 5,150 km |
Temperature And Pressure
The core’s temperature and pressure are extreme. The inner core’s temperature reaches up to 5,700°C. The outer core is slightly cooler but still very hot.
Pressure in the inner core is also immense. It can be as high as 3.6 million times the atmospheric pressure at sea level.
These extreme conditions make studying the core challenging but important for understanding Earth’s density.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Scientific Discoveries
Understanding Earth’s density helps scientists learn about its structure. The Earth’s density is a measure of how much mass is packed into a given volume. Various scientific methods have revealed amazing insights into Earth’s density. These discoveries span multiple disciplines and provide a detailed picture of our planet.
Seismic Studies
Seismic studies use waves generated by earthquakes. These waves travel through Earth and reveal its inner layers. There are two main types of seismic waves: P-waves and S-waves.
- P-waves: These are primary waves. They travel faster and move through both solid and liquid layers.
- S-waves: These are secondary waves. They only travel through solid layers.
By studying the speed and path of these waves, scientists can infer the density of Earth’s layers. Seismic waves slow down in less dense materials and speed up in denser ones.
Magnetic Field Insights
Earth has a magnetic field generated by its core. The core is made mostly of iron and nickel. This field provides clues about Earth’s density.
Scientists use satellites to measure the magnetic field. These measurements help determine the density of Earth’s core. The strength and variations in the magnetic field indicate the distribution of materials inside Earth.
The data collected from these methods contribute to our understanding of Earth’s density. Each discovery adds a piece to the puzzle, giving us a clearer view of our planet’s structure.
Implications Of Density
The density of Earth influences various aspects of our planet. From geological processes to the impact on life, understanding Earth’s density helps us grasp the planet’s dynamics.
Geological Processes
Earth’s density plays a critical role in geological activities. Dense materials sink towards the core, while lighter materials rise to the surface. This movement creates tectonic plates, which are responsible for earthquakes and volcanic activity. The distribution of these materials leads to the formation of mountains, valleys, and ocean basins.
Density differences also drive mantle convection. This process involves the slow creeping motion of Earth’s mantle caused by convection currents. It influences plate tectonics and contributes to the recycling of Earth’s crust.
Impact On Life
Density affects the distribution of elements and compounds essential for life. For instance, water has a lower density than rocks, allowing it to fill basins and create oceans. These bodies of water are crucial habitats for marine life and play a key role in Earth’s climate.
The density of Earth’s atmosphere also impacts life. It helps retain the right amount of heat, making the planet habitable. The atmosphere’s layers, varying in density, protect us from harmful solar radiation.
Gravity, influenced by Earth’s density, affects how organisms grow and move. Plants and animals have adapted to the gravitational pull, influencing their structure and behavior.
Credit: www.ucl.ac.uk
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Earth’s Average Density?
Earth’s average density is about 5. 52 grams per cubic centimeter.
How Is Earth’s Density Measured?
Earth’s density is measured using mass and volume calculations from gravitational data.
Why Is Earth Denser Than Other Planets?
Earth is denser due to its metallic core and rocky mantle.
What Affects Earth’s Density?
Earth’s density is affected by its composition and internal structure.
How Does Earth’s Density Compare To Other Planets?
Earth is the densest planet in our solar system.
Does Earth’s Density Change Over Time?
Earth’s density can change slightly due to geological processes and core cooling.
Conclusion
Understanding Earth’s density offers insight into its composition and structure. This knowledge helps us explore geological processes. By studying Earth’s density, we can better appreciate the planet’s complexities. Keep diving into science to uncover more fascinating facts about our world.
Stay curious and keep learning!
