Meth can stay in your system for 1-4 days. This varies based on factors like dosage and metabolism.
Methamphetamine, commonly known as meth, is a potent and highly addictive stimulant. It affects the central nervous system, leading to a rapid onset of euphoria and increased energy. The duration meth stays in the system depends on several factors, including the method of use, dosage, and an individual’s metabolic rate.
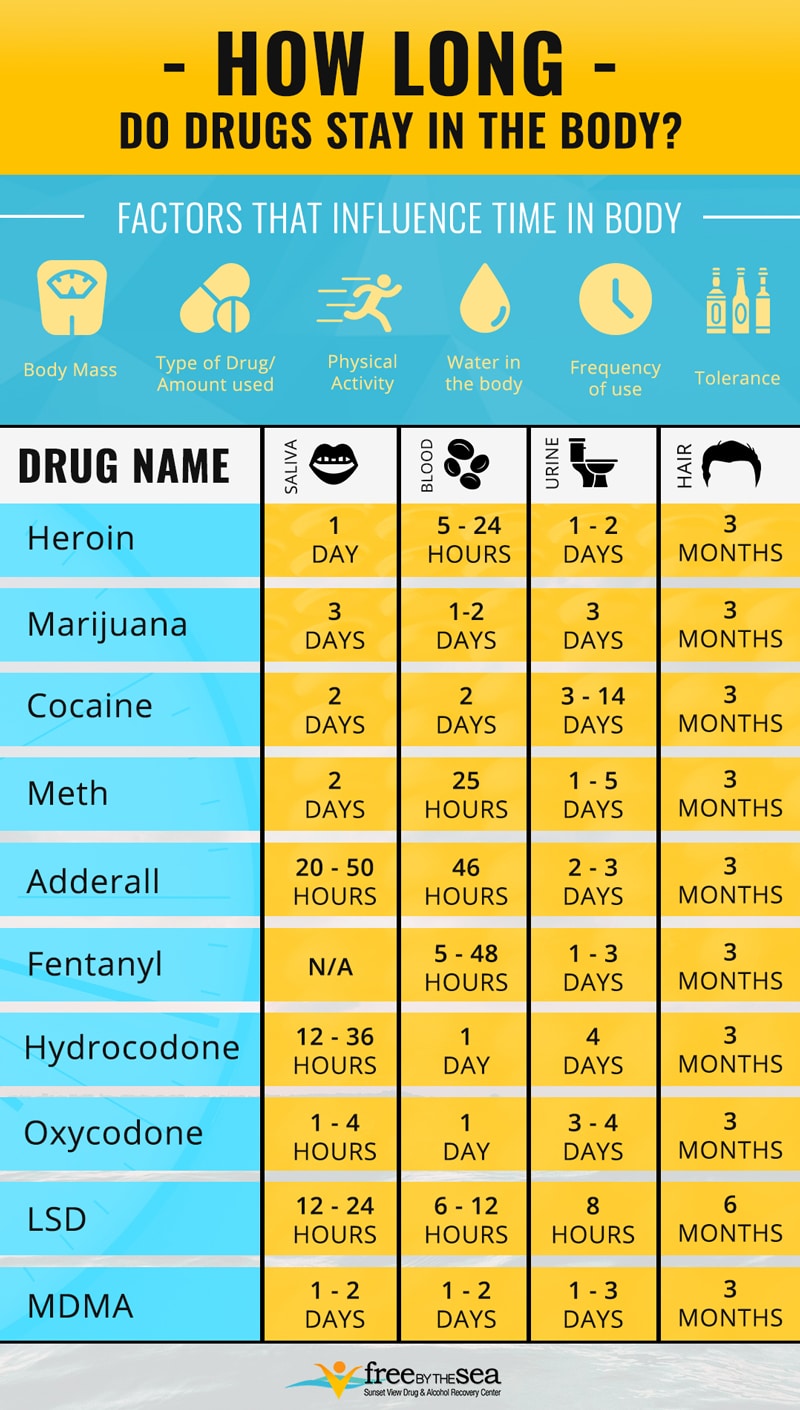
Detection times can vary across different tests, such as urine, blood, saliva, and hair. Understanding these timelines is crucial for those undergoing drug testing or seeking to detoxify. Staying informed about meth’s presence in the body can aid in making better health and lifestyle choices.
Meth Metabolism
Understanding meth metabolism helps in knowing how long it stays in the system. This process involves several stages, from absorption to excretion. Each stage impacts the duration meth remains detectable.
Absorption Process
Meth enters the body through various methods: smoking, snorting, injecting, or ingesting. Each method affects how quickly meth is absorbed.
- Smoking or injecting: Meth reaches the bloodstream within seconds.
- Snorting: Absorption takes a few minutes.
- Ingesting: The process can take 20-30 minutes.
Once in the bloodstream, meth travels to the brain, producing a quick and intense high.
Factors Influencing Metabolism
Several factors influence how quickly meth is metabolized and excreted:
| Factor | Impact on Metabolism |
|---|---|
| Age | Older individuals metabolize meth more slowly. |
| Body Mass | Higher body mass can slow metabolism. |
| Hydration | Better hydration speeds up excretion. |
| Frequency of Use | Frequent use leads to slower metabolism. |
These factors combined determine how long meth stays in the system. A typical range is 1-4 days, but it can vary.
Credit: freebythesea.com
Detection Windows
Understanding the detection windows for methamphetamine is crucial. This knowledge helps in various contexts, like medical testing and legal scenarios. Meth can be detected through several methods, such as urine and blood tests. Each method has its unique detection period.
Urine Testing
Urine testing is one of the most common methods for detecting meth. It is non-invasive and easy to administer. Urine tests can detect meth for up to 3-5 days after use. In chronic users, it can be detected for even longer periods.
Here is a table showing the detection window for different usage patterns:
| Usage Pattern | Detection Window |
|---|---|
| Single Use | 3-5 days |
| Chronic Use | Up to 7 days or more |
Blood Testing
Blood testing provides a shorter detection window. It is often used in emergency settings. Meth can be detected in the blood within 1-3 days. This method is more invasive compared to urine testing.
Blood tests are usually conducted when immediate results are needed. They are less common for routine drug screening.
To summarize:
- Urine tests: 3-5 days for single use, longer for chronic use.
- Blood tests: 1-3 days after use.
Knowing these detection windows can help you make informed decisions. Always consider the type of test and its detection period.
Impact On Different Systems
The effects of methamphetamine can be long-lasting and severe. Different systems in the body react differently to meth. Understanding this can help in managing its impact.
Central Nervous System
Meth greatly affects the central nervous system (CNS). It increases dopamine levels, causing intense euphoria. This can lead to addiction. Over time, meth damages brain cells. Users may experience memory loss, anxiety, and violent behavior. Chronic use can also cause Parkinson’s-like symptoms.
- Increased dopamine levels
- Memory loss
- Anxiety and violent behavior
- Parkinson’s-like symptoms
These effects can last long after stopping meth. Treatment is often required for recovery.
Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system also suffers from meth use. Meth raises heart rate and blood pressure. This can cause heart attacks and strokes. Chronic use can lead to permanent heart damage. Users may also experience irregular heartbeats.
| Effect | Duration |
|---|---|
| Raised heart rate | Several hours |
| High blood pressure | Several hours |
| Heart attacks | Long-term risk |
| Irregular heartbeats | Long-term risk |
Monitoring and treatment can help manage these risks.
Effects Of Long-term Use
Long-term methamphetamine use has severe effects on the body and mind. The damage can be extensive and life-altering. Understanding these effects is crucial for awareness and prevention.
Physical Health Consequences
Long-term meth use causes serious physical health issues. Users often suffer from severe weight loss due to decreased appetite.
Dental problems are common, known as “meth mouth.” Teeth decay rapidly, leading to tooth loss. Skin sores develop from constant scratching and poor hygiene.
Heart problems can also arise, including increased heart rate and blood pressure. These issues can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
Here’s a table summarizing the physical health consequences:
| Health Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Weight Loss | Decreased appetite leads to severe weight loss. |
| Dental Problems | Teeth decay rapidly, causing tooth loss. |
| Skin Sores | Sores develop from constant scratching. |
| Heart Problems | Increased heart rate can lead to heart attacks. |
Mental Health Implications
Meth use also affects mental health. Users often experience paranoia and anxiety. They may have hallucinations and delusions.
Memory loss is another significant effect. Users find it hard to recall recent events. Mood swings are common, leading to aggression.
Here are some key mental health implications:
- Paranoia and anxiety
- Hallucinations and delusions
- Memory loss
- Mood swings and aggression
Long-term meth use can lead to severe mental health issues. Early intervention is crucial for recovery.
Methods To Aid Elimination
Understanding how long meth stays in your system is crucial. Various methods can help eliminate meth faster. Below, we explore some effective methods to aid elimination.
Hydration And Diet
Drinking plenty of water helps flush out toxins. Staying hydrated can speed up the elimination process. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily.
- Include fruits and vegetables in your diet.
- Foods rich in antioxidants can aid detoxification.
- Avoid processed foods and sugary drinks.
A balanced diet supports your liver and kidneys. These organs are key in removing toxins from your body.
Medical Interventions
Medical interventions can also aid meth elimination. Consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
| Intervention | Description |
|---|---|
| Activated Charcoal | Can bind to toxins and help remove them. |
| IV Fluids | Hydrates the body and supports organ function. |
| Medications | Some drugs can aid in faster detox. |
These methods can be effective but should be used under medical supervision.
Credit: www.theedgetreatment.com
Credit: www.harmonyridgerecovery.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does Meth Stay In Your Urine?
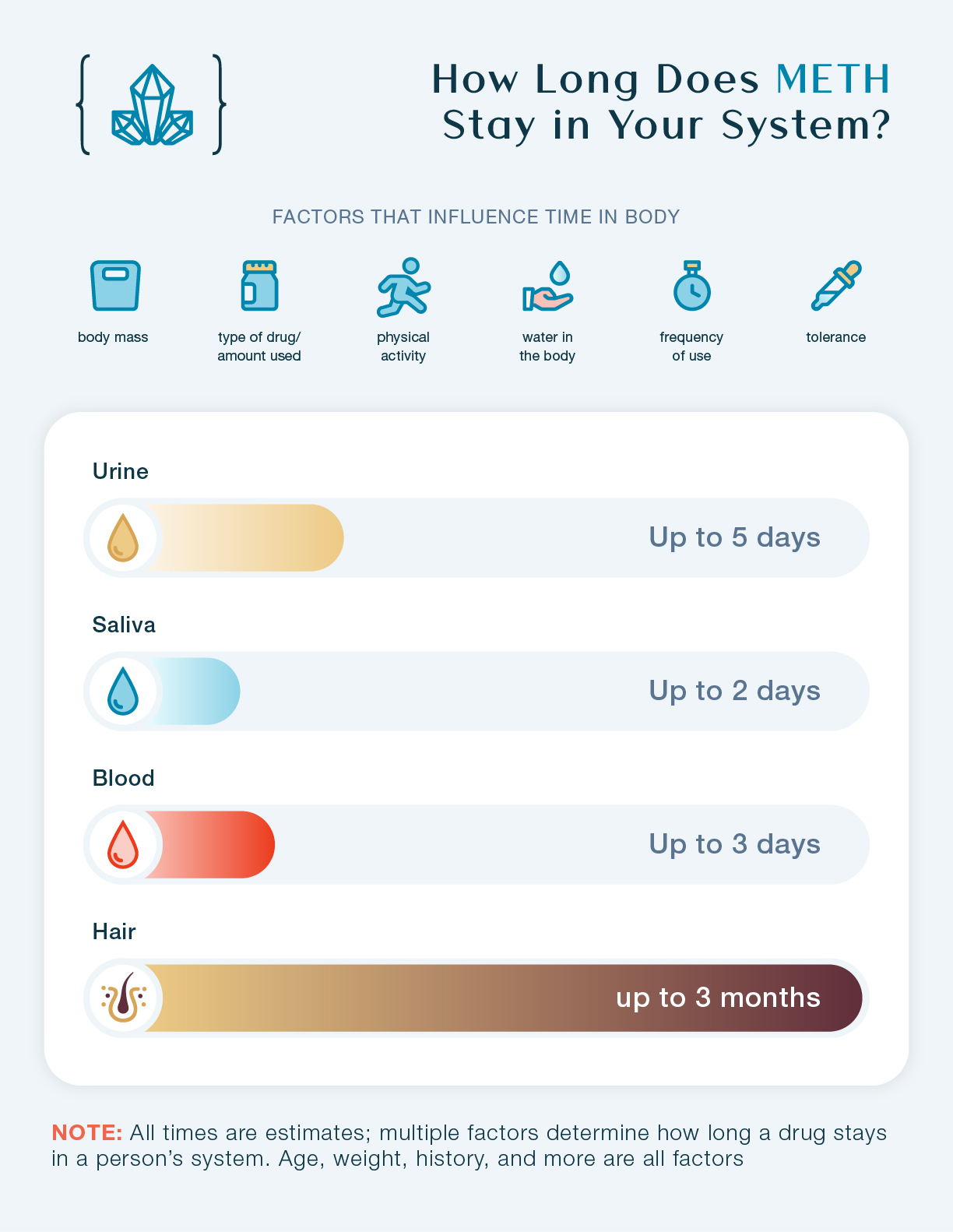
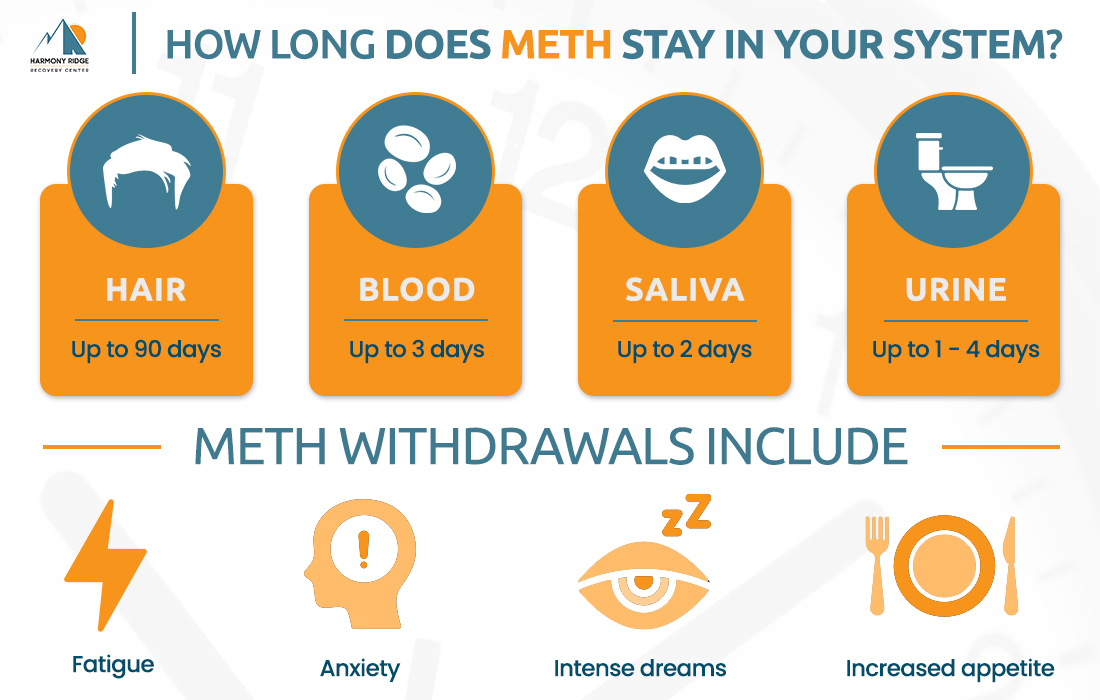
Meth can be detected in urine for up to 3-5 days. This timeframe may vary based on usage frequency, dosage, and individual metabolism.
How Long Does Meth Stay In Your Blood?
Meth is detectable in blood for approximately 1-3 days. Detection times can differ based on various factors like metabolism and dosage.
How Long Does Meth Stay In Your Saliva?
Meth can be detected in saliva for about 1-4 days. Saliva tests are often used for recent drug use detection.
How Long Does Meth Stay In Your Hair?
Meth can be detected in hair for up to 90 days. Hair tests are used for long-term drug use detection.
Conclusion
Understanding how long meth stays in your system is crucial for health and recovery. Various factors influence detection times. Being informed helps in making better choices. Always seek professional help for addiction issues. Stay educated and prioritize your well-being to lead a healthier life.
